Class 12th Notes On Fertilisation & Double Fertilisation

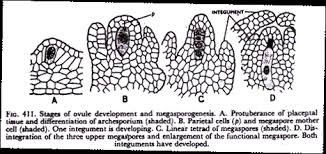
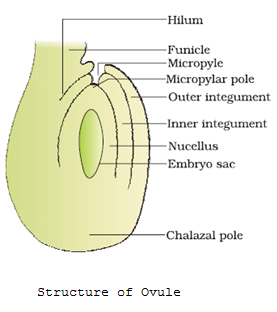
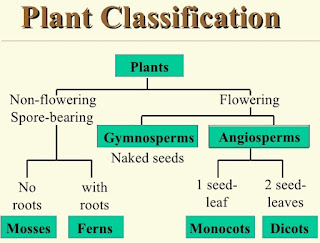
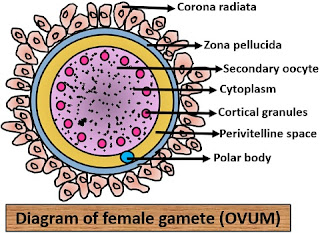
Fertilization In Angiosperm , fertilization or syngamy is the process of interaction of two opposite gamete for the formation of the zygote which later develops into an embryo . After fertilization the ovule forms the seed while ovary converts into fruit . Process - The pollen grain of the flower flow through the air or attached to the insects and reach to the flower . This pollen grain starts to germinate on the stigma of the female gametophyte and the pollen tube arises to develop through the style and reach to the ovule of the embryo sac . This pollen tube contains two cells ; generative cells and vegetative cells . The vegetative cells have a reserved food material through which generative cell mature and divides...