Genetic code - Principle, Features & Discovery | Biology Blog
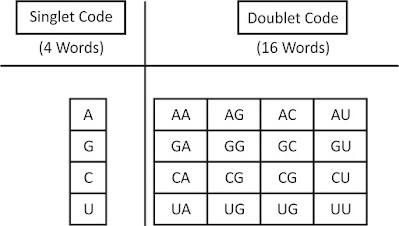
Genetic Code Any biochemical process is ended up by the arbitration of the enzymes. These enzymes are consist of proteins. Every protein is cover of at least 20 amino acids, whereas the DNA is made up of only four nucleotides. The four nitrogenous bases of DNA will tell you all 20 amino acid sequences. All the genetic information for a character is coded in the nucleotide of DNA called Codon. The sequence of nucleotide or nitrogenous bases in mRNA molecules which locked the information for protein synthesis and called as Genetic Code. Discovery - In 1968 Nirenberg, Khorana &Holley have discovered genetic code. Nirenberg also received a noble prize for success in genetic code. The problem in Genetic code - The major issue of genetic code was to resolve the perfect number of nucleotides in a codon t...