Cell biology notes on Golgi appratus
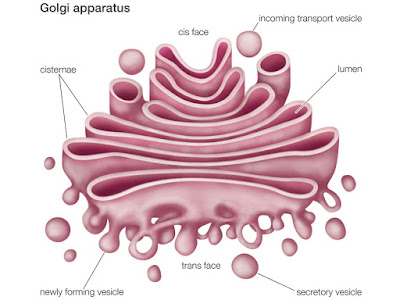
Golgi Complex The Golgi body is a membrane-bound organelle found in all the eukaryotic cells except RBCs. They remain scattered in the cytoplasm and called dictyosomes but in an animal cell they are localized. Camello Golgi in the year 1898 discovered it from the nerve cell of the cat and named it Golgi after discovery. It plays a significant role in the synthesis of large molecules of complex carbohydrates. Golgi Complex is also known by another name Lipchondria, Idiosome, Dalton Complex, and Golgi Apparatus. Also, refer - Golgi body Role Of Golgi Complex - Golgi Complex is responsible for transporting and packaging of protein & lipid molecules into vesicles for delivery to the target destination. Origin - It is believed that Golgi Body arises from the vesicle of the endoplasmic reticulum....
