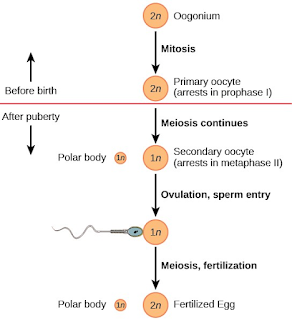
4 Phases Of Menstrual Cycle & Ovulation In Females

Menstruation cycle Every month, females undergo a natural reproductive cycle. During this cycle, the body prepares itself for a possible pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the body sheds the prepared uterine lining and resets the cycle for the next month. This process begins at puberty, a stage known as menarche , and continues until a woman reaches the age of approximately 40 to 50 years , when the cycle gradually comes to an end — a phase known as menopause . Duration - Generally, the duration of this cycle is ideally 28 days, but in some cases, its duration extends from 28 to 32 . Phases - This cycle is completed in four phases - ...