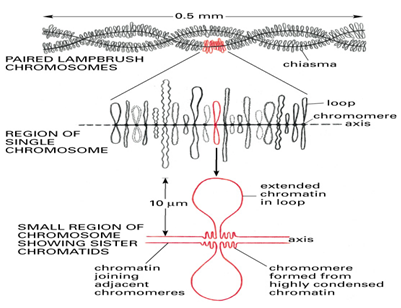
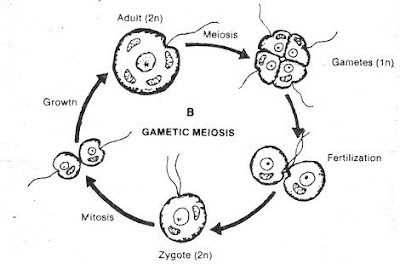
Bruce Ames Contribution In Oncology
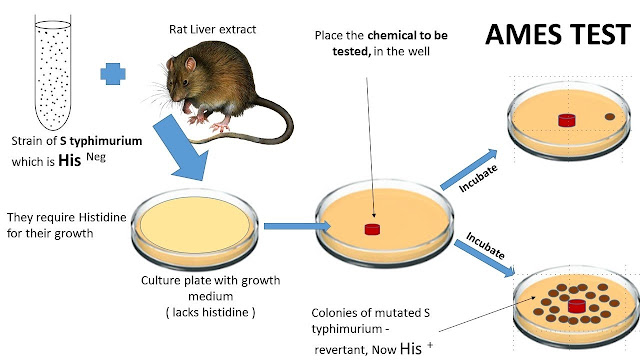
Ames Test Bruce Ames develops a method to test the chemicals for cancer causing properties . The test is based on the fact that any thing that is mutagenic may also turn out to be a carcinogen, that is to cause cancer . The assay is based on the reversion of the mutation in the histidine operon in the genetically altered tester strains of bacterium Salmonella typhimurium . The his peron encodes enzymes required for the biosynthesis of the amino acid hitsidine . Strains with mutations in the his operon are histidine auxotrophs . However , the mutation can be reversed , a back mutation , with the gene...