Brief notes on Oogenesis with 3 phases
Oogenesis
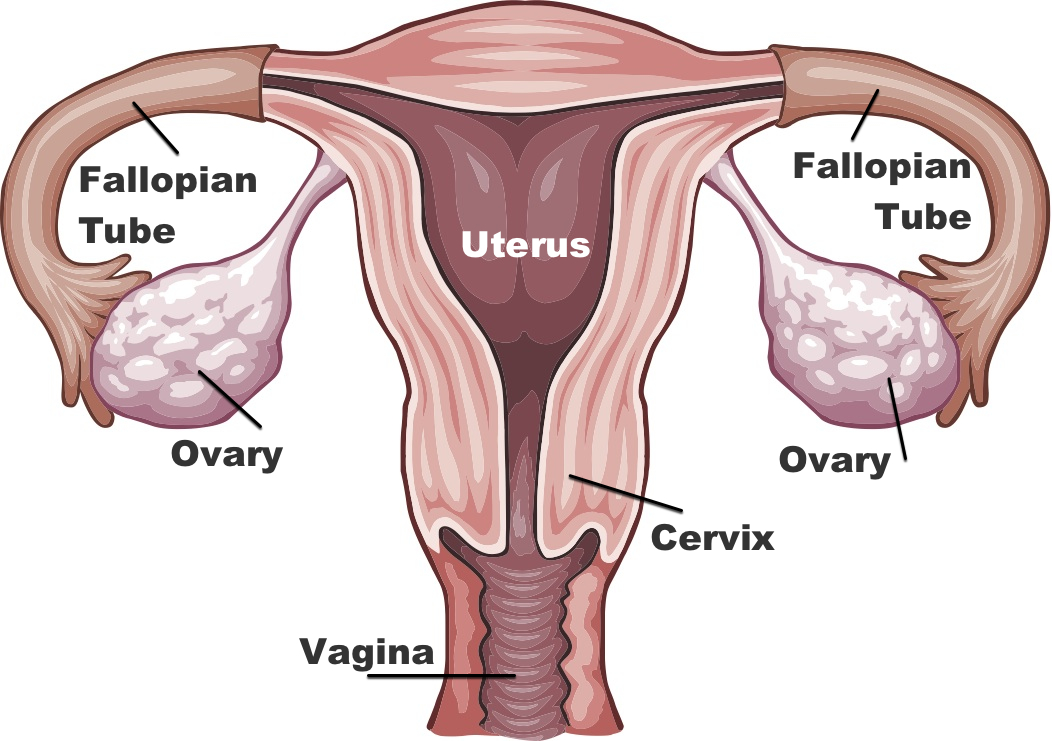
The process of formation of the female egg is known as oogenesis. The process takes place in ovaries. Generally, in most higher organisms, this process starts when the female fetal is developing in the womb. The whole process can be studied in three phases -
-
Multiplication Phase
-
Growth Phase
-
Maturation Phase
- Multiplication phase - In the fetal embryo, the ovum mother cell or we can say oogonia start to multiply through mitosis and a large number of diploid oogonia i.e., millions of oogonia are produced.
- Growth Phase - Like spermatogenesis, oogonia grow in their size and shape to form primary oocyte with a diploid number of chromosomes. If we talk about other higher animals except for human then this phase is one of the largest phases of oogenesis. During the growth phase, several changes occur in egg and all these changes are classified into two subcategories -
- vitellogenesis
-
Previtellogenesis - A number of changes occur in the nucleus and cytoplasm like the number of nucleoplasm increases, the nucleolus increases. Likewise, the number of cell organelle increases in cytoplasm, specially Golgi body, ER, mitochondria become increases in large numbers. Later all these three organelles arrange in a ring-like structure around the nucleus and there is a formation of the Balbiani Vitelline Ring. Space appears in between the plasma membrane of the egg and vitelline membrane called perivitelline space in which a fluid is filled called perivitelline fluid.
- Vitellogenesis - Now egg starts storing food in the form of yolk.
- Maturation Phase - The primary oocyte starts its meiotic division in the fetal embryo but gets arrested in prophase the first stage of meiosis. In this way, in a newborn girl, there is 2 lakh primary oocyte present in her ovary. When a girl attains a puberty stage than one of the ovaries stimulates only one primary oocyte for resuming meiosis first with the help of follicular stimulating hormone or FSH. After completing meiosis first, the primary oocyte form two cell one is larger than another cell. Larger cell is known as a Secondary Oocyte and smaller one is known as Polar body. This secondary oocyte again started meiosis second but get arrested in metaphase second stage of meiosis. It then stops further and waits for the sperm to complete the further process of the meiotic division. After the entrance of sperm in the fallopian tube cell cycle again started by breaking the M phase promoting f tor or MPF and turning on the anaphase-promoting complex. Completion of meiosis second converts the secondary oocyte into a fertilized egg or zygote and also a second polar body.



Thank you for the helpful blog, "Brief notes on Oogenesis with 3 phases." I want you to know that your information is invaluable for aspiring candidates. Keep sharing valuable updates!
ReplyDeleteChandu Biology Classes